Components of the Computer Motherboard
Updated: February 12, 2024
112
As the component that connects every other component of a computer system, the motherboard is an essential component. It is often referred to as the mainboard or system board. Where each part serves as a hobby and is essential to the operation of your digital experience. Together, let’s set out on an adventure to explore the welcoming landscape of motherboard components. We’ll demystify every component with ease and warmth, from the RAM slots that power the mind’s memories to the CPU socket that acts as its connectivity. Acquire a gift to comprehend the inner workings of your computer like never before.
Types of Computer Motherboard
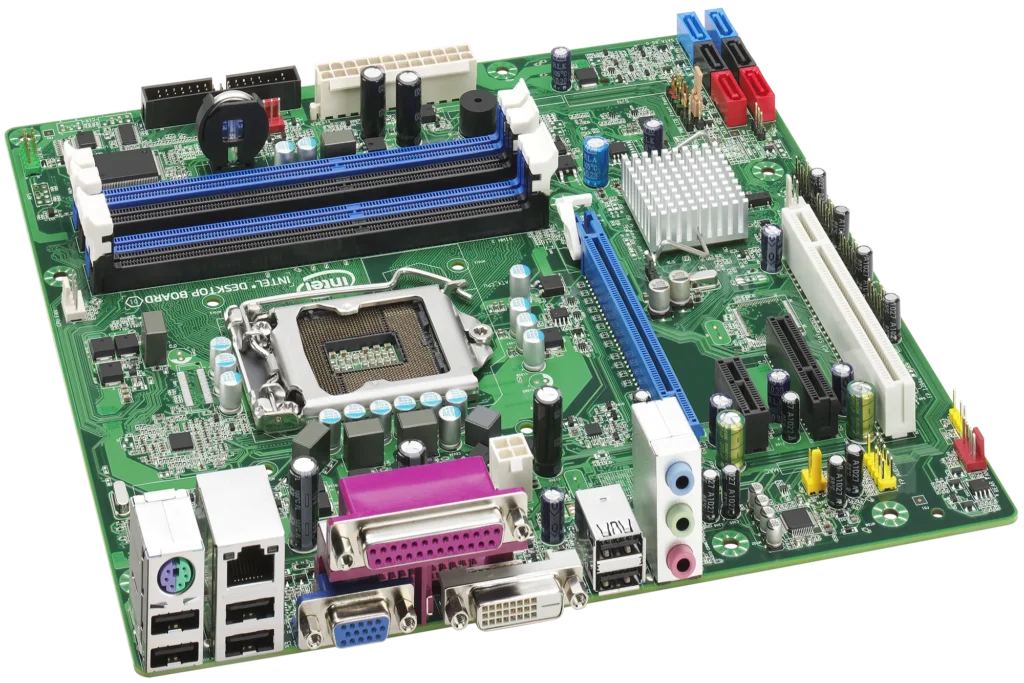
A variety of motherboard types are available, including ATX, Micro-ATX, Mini-ITX, and BTX motherboards Pico BYX motherboards, etc. These types change in size and features, with few offering more slots and connectors for Components In the century 1980s, motherboards of this sort were all the rage, and they continued to be manufactured far into the 2000s.
There are several types of motherboards available, such as ATX, Micro-ATX, Mini-ITX, BTX motherboard Pico BYX motherboards, etc. These types change in size and features, with few offering more slots and connectors for Components In the century 1980s, motherboards of this sort were all the rage, and they continued to be manufactured far into the 2000s.
Standard ATX Motherboard
The standard-size motherboard commonly used in desktop computers adheres to the ATX (Advanced Technology Extend) form factor specifications consolidated by Intel. ATX motherboards are widely used in desktop computers and offer a standardized layout and size, making them compatible with most ATX-compatible computer trials.
Factor
The basic ATX form factor is normally 12 by 9.6 inches (305 x 244 mm), while smaller cases are available with microATX and mini-ITX variants.
Expansion Slots
It provides multiple expansion slots for network, sound, and graphics cards, among other components. PCI Express x16 slots are used for graphics cards, whereas PCIe x1 slots are used for other peripherals.
Power Supply Connector
ATX motherboards feature a 24-pin power connector, providing power to the motherboard from the power-provide unit (PSU).
Micro ATX Motherboard
Is a motherboard with a lower factor that is more portable than ATX but still has some functionality and expansion slots for desktop PCs It incorporates many of the capabilities sought after in knowledgeable ATX motherboards, all while fitting into compact computer cases. A few features of Micro ATX motherboards are as follows:
Form Factor
Smaller in size than conventional ATX boards are micro ATX motherboards.
Slots for Expansion
Even though Micro ATX motherboards are smaller than regular ATX boards, they nevertheless have multiple expansion slot
Power Supply Connector
Like knowledge ATX motherboards, Micro ATX boards feature a 24-pin force connector, which connects to the force supply unit (PSU) to supply power to the motherboard.
Mini ITX Motherboard
The smallest form-factor motherboard commonly used in small-factor PCs, offering fewer expansion slots and features but saving space
RAM Slots
Mini ITX motherboards typically introduce two RAM slots for installing memory modules. This permits for a limited amount of memory compared to larger form factor motherboards but is sufficient for often mainstream computing works.
I/O Ports
Despite their small size, Mini ITX motherboards support a variety of input/output ports, including USB, Ethernet, audio jacks, HDMI, and DisplayPort. The number and style of ports may vary depending on the specific motherboard model. Processor Socket: Mini ITX motherboards support a specific type of CPU socket, such as AMD’s PGA (Pin Grid Array) or Intel’s LGA (Land Grid Array), allowing compatibility with compatible processors.
BTX Motherboard
A legacy from-factor motherboard design intended to improve airflow and cooling in PCs but not widely used anymore BTX motherboards were intended to address certain limitations of the ATX form factor, particularly in terms of thermal tactics and component placement.
Form Factor
BTX motherboards have a different physical layout compared to ATX motherboards. The BTX form factor is designed to improve airflow and thermal management within the computer lawsuit by rearranging the positions of components.
Layout
In a BTX motherboard, the CPU socket is typically located closer to the front of the case, while the expansion slots are positioned towards the rear. This permits for other efficient airflow over the CPU and expansion cards.
Cooling Solutions
BTX motherboards must include provisions for improved cooling solutions, such as larger heatsinks and heat pipes, to better finish heat generated by the CPU and more points. Additionally, BTX cases may feature dedicated airflow channels to direct cool air over hot components.
Pico BTX Motherboard
A smaller version of the BTX design that never gained widespread adoption in the market
Slots for Expansion
Even though Micro ATX motherboards are smaller than regular ATX boards, they nevertheless have multiple expansion slots
Power Supply Compatibility
Pico BTX motherboards are designed to work with specialized power supplies that are compatible with the smaller form factor. These power supplies are typically smaller and have lower wattage compared to standard ATX power supplies.
Compatibility
Pico BTX motherboards and cases are less common than standard ATX or even BTX components. They are often used in specialized applications where space is at a premium, such as industrial computers, embedded systems, or small form factor desktops.
Overall where space constraints are a primary consideration. They provide a balance between performance and size, making them suitable for a variety of specialized applications. Each of these motherboard types differs in size features and compatibility with computer cases and components
The Parts of a Motherboard and How They Work
The CPU socket, RAM slots, expansion slots, chipset, BIOS, connections, and force connectors are among a motherboard’s primary parts. Every part is essential to the motherboard’s operation and the computer’s overall performance.
A motherboard’s duties include giving the components force, permitting communication between them, managing data flow from the CPU to the memory, and facilitating connectivity with external devices. The motherboard, which allows all parts of a computer system to function together flawlessly, is essentially the spinal cord of the system.
Conclusion
The motherboard is like the heart of a computer, connecting and coordinating all its components to work together seamlessly. Just like a puzzle, it homes vital parts CPU sockets, RAM slots, and expansion slots, ensuring every piece finds its place. The CPU socket acts as the mind, processing instructions and executing jobs, while the RAM slots supply short-term memory for quick access to data. Expansion slots have the most room for upgrades, allowing users to customize their systems with graphics cards, sound cards, etc. Together, these components form a cohesive unit, powering the computer’s functionality and enabling users to accomplish work efficiently.
FAQS (Frequently Asked Questions)
What constitutes a motherboard’s core parts?
The three primary motherboard types—ATX, Micro-ATX, and Mini-ITX—variate in terms of features and volume. The normal size of the ATX motherboard leaves plenty of room for extra parts and accessories. While the Mini-ITX is also smaller and more suited for compact form factor computers, the Micro-ATX is larger and better suited for sturdy designs. Different needs and preferences are met by different motherboard types.
What are the types of motherboards?
A variety of motherboard types are available, including ATX, Micro-ATX, Mini-ITX, BTX, Pico, and BYX motherboards. A handful of these varieties have additional slots and connectors for components, but their sizes and functions vary. These kinds of motherboards were quite popular in the 1980s.
What other name would one give a motherboard?
A mainboard or system board is another term for a motherboard. It connects all the vital parts of a computer, acting as its equivalent to the spinal cord. A computer motherboard’s primary parts are the CPU socket and memory.
What is the motherboard’s primary purpose?
Providing communication and force distribution between all of a computer’s components is the motherboard’s primary job. It facilitates smooth system operation, regulates data flow, and permits communication between the CPU, memory, and other devices. A motherboard is essential to the proper operation of a computer. Thus, keep in mind to give thanks to the motherboard the next time you turn on your computer to keep everything linked and operating smoothly.
What other name would one give a motherboard?
A mainboard or system board is another term for a motherboard. It connects all the vital parts of a computer, acting as its equivalent to the spinal cord. A computer motherboard’s primary parts are the CPU socket and memory.
Please Write Your Comments